Sleep quality and its associated factors among teachers

This research article highlighted the prevalence and factors associated with poor sleep quality among secondary school teachers in Selangor, Malaysia. This was a cross-sectional study that was conducted in two phases. Phase I tested the reliability of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index in the Malay language (M-PSQI), and Phase II determined the prevalence and factors associated with poor sleep quality among 1,871 secondary school teachers. Participants were recruited using a multistage sampling technique. A self-administered questionnaire was used to collect information on socio-demographic, teaching characteristics, comorbidities and characteristics of sleep. Additionally, the validated M-PSQI was used to measure sleep quality, and a Depression Anxiety Stress Scale-21 was used to measure mental health status. Results showed that the M-PSQI had a good internal consistency and moderate reliability. The prevalence of poor sleep quality was 61 (95% CI: 54-67)%. Total teaching hours/day, depression and stress were significantly associated with poor sleep quality in the univariate analysis, while only stress (OR 1.04; 95% CI 1.02-1.05%) remained significant in the multivariate analyses. In conclusion, stress level of the secondary school teachers should be reduced to improve sleep quality.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29848899/
Metabolic syndrome among non-obese adults in the teaching profession in Melaka, Malaysia

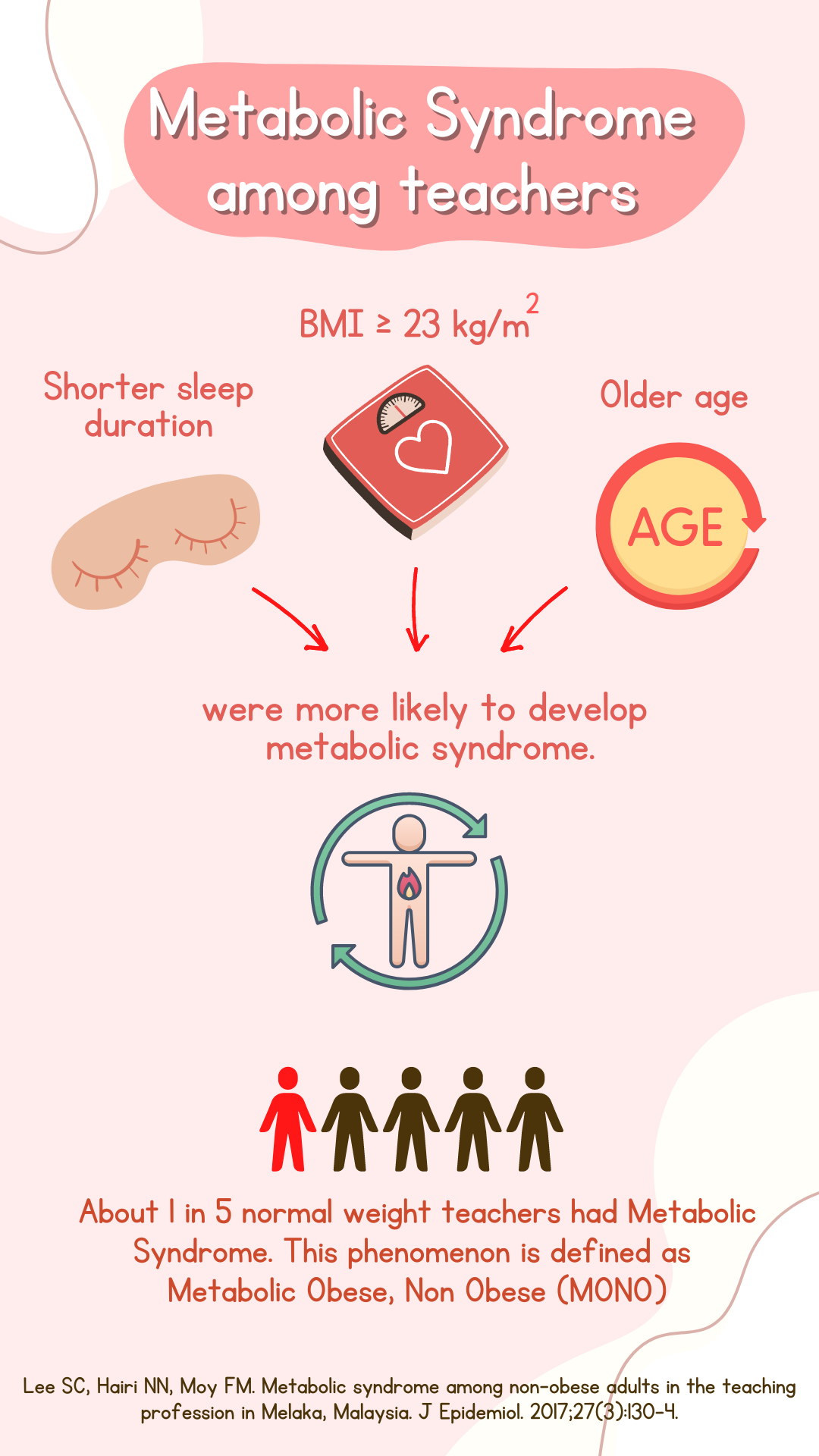
This study aimed to describe the prevalence and distribution of metabolically obese, non-obese (MONO) individuals in Malaysia. Metabolic syndrome was defined using the harmonization criteria as having any three or more of the following risk factors: central obesity, elevated triglyceride, low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, high blood pressure, and high fasting blood glucose. Research findings showed that participants with BMI ≥23.0 kg/m2, shorter sleep duration and older age had significantly higher odds of metabolic syndrome. The prevalence of metabolic obese, non-obese (MONO) was 17.7% among the teacher population.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5350617/
Determinants and Effects of Voice Disorders among Secondary School Teachers in Peninsular Malaysia Using a Validated Malay Version of VHI-10

This study was conducted to establish the prevalence of voice disorder using the Malay-Voice Handicap Index 10 (Malay-VHI-10) and to study the determinants, quality of life, depression, anxiety, and stress associated with voice disorder among secondary school teachers in Peninsular Malaysia. Findings from this study show that the Malay-VHI-10 is valid and reliable. Voice disorder was associated with increased absenteeism, marginally associated with reduced health-related quality of life as well as increased anxiety among teachers.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26540291/
Cardiometabolic risks profile of normal weight obese and multi-ethnic women in a developing country

This study aimed to determine possible factors associated with ‘normal weight obesity’ among women in Peninsular Malaysia. ‘Normal weight obesity’ is characterized by high body fat accumulation around the waist or internal organs despite having a normal body mass index (BMI). (For normal-weight women, healthy percent body fat should range from 20% to 35%. For normal-weight men, the body fat percentage should lie from 8% to 25%) In this study, ‘normal weight obesity’ is more commonly seen among older women or Indians. Further findings show that ‘normal weight obesity’ individuals had a higher rate of adverse health conditions, namely abdominal obesity, high triglyceride level, and high blood pressure.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25987469/
